Matrix
A matrix is simply a set of numbers arranged in a rectangular table.

There are several types of matrices, but the most commonly used are:
- Rows Matrix
- Columns Matrix
- Rectangular Matrix
- Square Matrix
- Diagonal Matrix
- Scalar Matrix
- Identity Matrix
- Triangular Matrix
- Null or Zero Matrix
- Transpose of a Matrix
Row Matrix:
A matrix is said to be a row matrix if it has only one row.

Column Matrix:
A matrix is said to be a column matrix if it has only one column.

Rectangular Matrix:
A matrix is said to be rectangular if the number of rows is not equal to the number of columns.

Square Matrix:
A matrix is said to be square if the number of rows is equal to the number of columns.
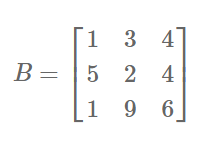
Diagonal Matrix:
A square matrix is said to be diagonal if at least one element of principal diagonal is non-zero and all the other elements are zero.

Scalar Matrix:
A diagonal matrix is said to be scalar if all of its diagonal elements are the same.
Identity or Unit Matrix:
A diagonal matrix is said to be identity if all of its diagonal elements are equal to one, denoted by I.

Triangular Matrix:
A square matrix is said to be triangular if all of its elements above the principal diagonal are zero (lower triangular matrix) or all of its elements below the principal diagonal are zero (upper triangular matrix).

Null or Zero Matrix:
A matrix is said to be a null or zero matrix if all of its elements are equal to zero. It is denoted by O.

Transpose of a Matrix:
Suppose A is a given matrix, then the matrix obtained by interchanging its rows into columns is called the transpose of A. It is denoted by At.

Determinants of a matrix
The determinant of a matrix is a special number that can be calculated from a square matrix.
For a 2×2 Matrix
For a 2×2 matrix (2 rows and 2 columns):


For a 3×3 Matrix
For a 3×3 matrix (3 rows and 3 columns):

Adjoint of a Matrix
Let A=[aij] be a square matrix of order n. The adjoint of matrix A is the transpose of the cofactor matrix of A. It is denoted by adj A. An adjoint matrix is also called an adjoint matrix.
Example:

To find the adjoint of a matrix, first find the cofactor matrix of the given matrix. Then find the transpose of the cofactor matrix.


Inverse of a matrix
The inverse of A is A-1 only when:
A × A-1 = A-1 × A = I
Sometimes there is no inverse at all.
Formula:
Multiplication of a matrix

